The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence:
Unleashing the Power of Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has undergone a remarkable evolution in recent years, transforming the landscape of technology and reshaping the way we approach problem-solving across various domains. At the heart of this evolution lies the revolutionary field of Machine Learning (ML), where computers learn from data to improve their performance over time. In this article, we will delve into the advancements in AI and explore the diverse applications of machine learning across different sectors.
Evolution of AI: From Concept to Reality
Early Days of AI:
Artificial Intelligence, as a concept, dates back to ancient times. However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that the term gained prominence with the advent of electronic computers. Early AI research focused on symbolic reasoning and problem-solving, laying the groundwork for future developments.
Machine Learning Emergence:
The emergence of Machine Learning marked a significant paradigm shift. Instead of relying on explicit programming, ML systems could now learn patterns and make predictions from data. This shift led to the development of various machine learning algorithms, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
Deep Learning Revolution:
In recent years, Deep Learning has propelled AI to new heights. Based on neural network architectures, deep learning algorithms mimic the human brain’s structure, enabling them to process vast amounts of data and extract intricate patterns. This approach has fueled breakthroughs in image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and more.
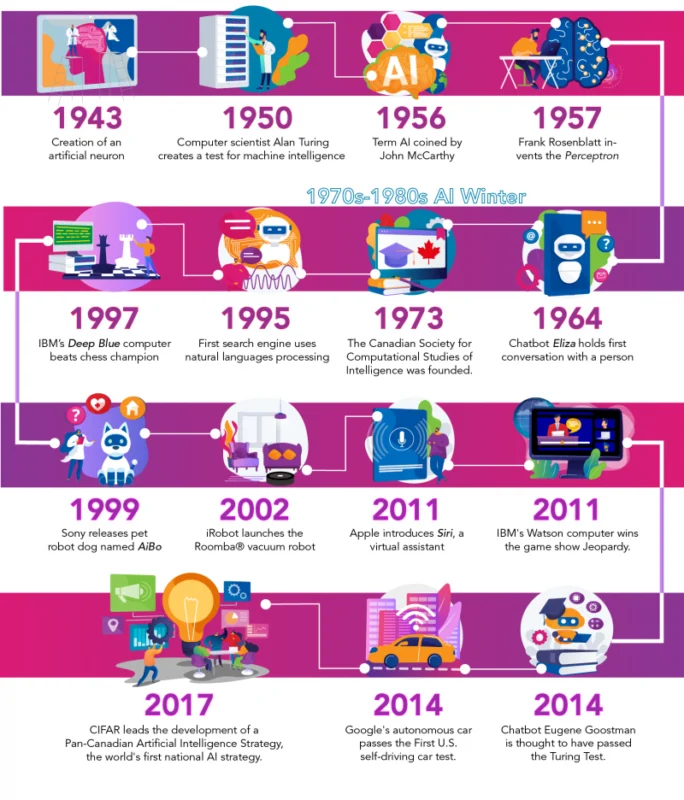
AI timeline (Let’s Talk Science using multiple images by Visual Generation via iStockphoto).
|
Brief History of Artificial Intelligence |
|
| 1943 | Warren S. McCulloch and Walter Pitts create a model for an artificial neuron based on human neurons. |
| 1950 | Computer scientist Alan Turing creates a test for machine intelligence. He called it “the imitation game.” It is now known as the “Turing Test.” |
| 1956 | The phrase Artificial Intelligence was first published by computer scientists John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky. |
| 1957 | Frank Rosenblatt invents the Perceptron. It is the first computer neural network based on the human brain. |
| 1964 | The first chatbot, Eliza, holds conversations with humans. |
| 1970s-1980s | Pessimism about machine learning and a lack of funding leads to the ‘AI Winter‘. |
| 1973 | The Canadian Society for Computational Studies of Intelligence is founded by researchers across the country. This is now called the Canadian Artificial Intelligence Association. It is located at Western University. |
| 1995 | AltaVista is the first search engine to use natural language processing. |
| 1997 | IBM’s Deep Blue is the first computer to beat a chess champion. It defeats Russian grandmaster Garry Kasparov. |
| 1999 | Sony launches a robot pet dog named AiBO. It’s skills and personality develop over time. |
| 2002 | iRobot launches the Roomba® floor-vacuuming robot. |
| 2011 | Apple integrates Siri, an intelligent virtual assistant, into the iPhone 4S. |
| 2011 | IBM’s Watson computer wins at the TV game show Jeopardy. This proved it could understand complex human language, because questions included word play. |
| 2014 | Some experts think computer “chatbot” Eugene Goostman has passed the Turing Test. |
| 2014 | Google’s self-driving car passes the Nevada state self-driving car test. |
| 2017 | CIFAR leads the development of a Pan-Canadian Artificial Intelligence Strategy, the world’s first national AI strategy. |
Applications of Machine Learning Across Industries
Healthcare:
- Diagnostics and Imaging:
- Name: IBM Watson Health
- Description: IBM Watson Health utilizes machine learning to analyze medical images, aiding in the early detection of diseases such as cancer.
- Name: IBM Watson Health
- Drug Discovery:
- Name: Atomwise
- Description: Atomwise employs AI for drug discovery, predicting potential drug candidates by analyzing molecular structures.
- Name: Atomwise
Finance:
- Fraud Detection:
- Name: Feedzai
- Description: Feedzai’s machine learning algorithms detect and prevent fraudulent transactions in real-time by analyzing transaction patterns.
- Name: Feedzai
- Algorithmic Trading:
- Name: QuantConnect
- Description: QuantConnect uses machine learning to develop and optimize algorithmic trading strategies based on market trends.
- Name: QuantConnect
Education:
- Personalized Learning:
- Name: DreamBox
- Description: DreamBox employs machine learning to create personalized learning paths for students, adapting to their individual strengths and weaknesses.
- Name: DreamBox
- Automated Grading:
- Name: Gradescope
- Description: Gradescope uses AI to automate the grading process, providing quick and accurate feedback to students.
- Name: Gradescope
Retail:
- Recommendation Systems:
- Name: Amazon’s Recommendation Engine
- Description: Amazon’s machine learning-powered recommendation system analyzes user behavior to suggest personalized product recommendations.
- Name: Amazon’s Recommendation Engine
- Inventory Management:
- Name: Blue Yonder
- Description: Blue Yonder’s machine learning algorithms optimize inventory management, reducing stockouts and overstock situations.
- Name: Blue Yonder
Manufacturing:
- Predictive Maintenance:
- Name: Predictronics
- Description: Predictronics utilizes machine learning for predictive maintenance, forecasting equipment failures and minimizing downtime.
- Name: Predictronics
- Quality Control:
- Name: Sight Machine
- Description: Sight Machine’s AI-driven platform enhances quality control by analyzing production data for defects and anomalies.
- Name: Sight Machine
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
While the progress in AI and machine learning is undeniable, challenges such as ethical considerations, bias in algorithms, and data privacy issues persist. Striking a balance between innovation and responsibility remains a crucial aspect of the ongoing AI journey.
In conclusion, the evolution of AI, powered by machine learning, continues to reshape industries and redefine the boundaries of what is possible. As we navigate this ever-changing landscape, the collaboration between human intelligence and artificial intelligence holds the key to unlocking unprecedented potential and addressing the complex challenges of our time.

Certainly! Here are examples of AI application names across different domains:
If you’re looking for AI applications with names similar to ChatGPT , which is a language model, here are some examples:
- ConvoBotAI
- TalkGeniusAI
- TextCraftAI
- ConverseMindAI
- ChatterBotX
- DialogMasterAI
- LinguaTalkAI
- SpeakWiseAI
- DiscourseMateAI
- LanguageFlowBot
- SynthSpeakAI
- ChatSynthX
- CogniConvoAI
- VerbalSenseBot
- TextDynamoAI
- LingoLogicAI
- ConvoCraftAI
- SpeechCraftBot
- DialogForgeAI
- TextualMindAI
These names are designed to convey the idea of conversational AI or text-based interactions, similar to the capabilities of ChatGPT. Keep in mind that naming can be subjective, and the choice may depend on the specific focus or branding you have in mind for your AI application.
Certainly! Here are examples of AI application names across different domains:
- CogniHealth
- DataSageAI
- MediMindBot
- RoboGuardian
- EduSynthAI
- RetailRover
- AutoPilotDrive
- AgriBrain
- CyberShieldAI
- SmartRecruitBot
- LingoLinker
- MoneyMentorAI
- VirtuLearnAI
- HealthPulseAI
- EcoSenseBot
- TravelIntelAI
- SafetyNetGuard
- EntertainMateAI
- GreenHarborAI
- InnoLogicX
- SpeakUpAI
- SecureSphereBot
- CareSyncAI
- TradeCraftBot
- EnviroWatchAI
These names are designed to convey the essence of the AI applications in their respective domains. Keep in mind that choosing a name involves considering your branding strategy, target audience, and the specific focus of your AI application.
Certainly! Here are examples of AI applications across various domains:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Examples include Google Assistant, Siri, and chatbots on websites that provide instant customer support.
- Healthcare:
- Disease Prediction and Diagnosis: IBM Watson Health uses AI for analyzing medical images to assist in early disease detection.
- Personalized Medicine: AI algorithms analyze patient data to tailor treatment plans based on individual genetic profiles.
- Finance:
- Fraud Detection: Companies like Feedzai use AI to analyze transaction patterns and detect fraudulent activities.
- Robo-Advisors: AI-powered financial advisors, such as Wealthfront and Betterment, provide automated investment advice.
- Education:
- Personalized Learning: Platforms like DreamBox use AI to create personalized learning paths for students.
- Language Learning Apps: AI-powered apps like Duolingo adapt to users’ proficiency levels and learning styles.
- Retail:
- Recommendation Systems: Amazon’s recommendation engine suggests products based on user behavior.
- Dynamic Pricing: AI helps retailers optimize pricing based on demand, competitor prices, and other factors.
- Manufacturing:
- Predictive Maintenance: Companies like Predictronics use AI to predict equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules.
- Quality Control: AI systems analyze production data for defects and anomalies, improving product quality.
- Autonomous Vehicles:
- Self-Driving Cars: Companies like Tesla and Waymo use AI algorithms for autonomous navigation.
- Traffic Management: AI optimizes traffic flow in smart cities to reduce congestion.
- Agriculture:
- Precision Farming: AI analyzes data from sensors and satellites to optimize farming practices.
- Crop Monitoring: Drones equipped with AI monitor crop health and identify potential issues.
- Customer Service:
- Chatbots: Many websites use AI-driven chatbots for instant customer support.
- Virtual Assistants: AI-powered virtual assistants enhance customer interactions and streamline services.
- Cybersecurity:
- Threat Detection: AI analyzes network data to detect and respond to cybersecurity threats.
- User Authentication: AI is used for biometric authentication and fraud prevention.
- Energy:
- Smart Grids: AI optimizes energy distribution and consumption in power grids.
- Energy Forecasting: AI predicts energy demand, helping utilities plan and manage resources.
- Human Resources:
- Recruitment: AI assists in resume screening and candidate matching.
- Employee Engagement: AI analyzes employee data to improve engagement and productivity.
- Language Translation:
- Real-Time Translation: Google Translate and other tools use AI for instant translation of text and speech.
- Multilingual Content Creation: AI helps generate content in multiple languages.
- Entertainment:
- Content Recommendation: Streaming services like Netflix use AI to recommend movies and TV shows.
- Video Game AI: AI enhances gaming experiences through adaptive gameplay and intelligent opponents.
- Environmental Monitoring:
- Climate Modeling: AI models analyze climate data to predict and understand environmental changes.
- Wildlife Conservation: AI is used to monitor and protect endangered species.
These examples illustrate the wide-ranging impact of AI across industries, showcasing its versatility and potential for innovation.

